- Medical Stability
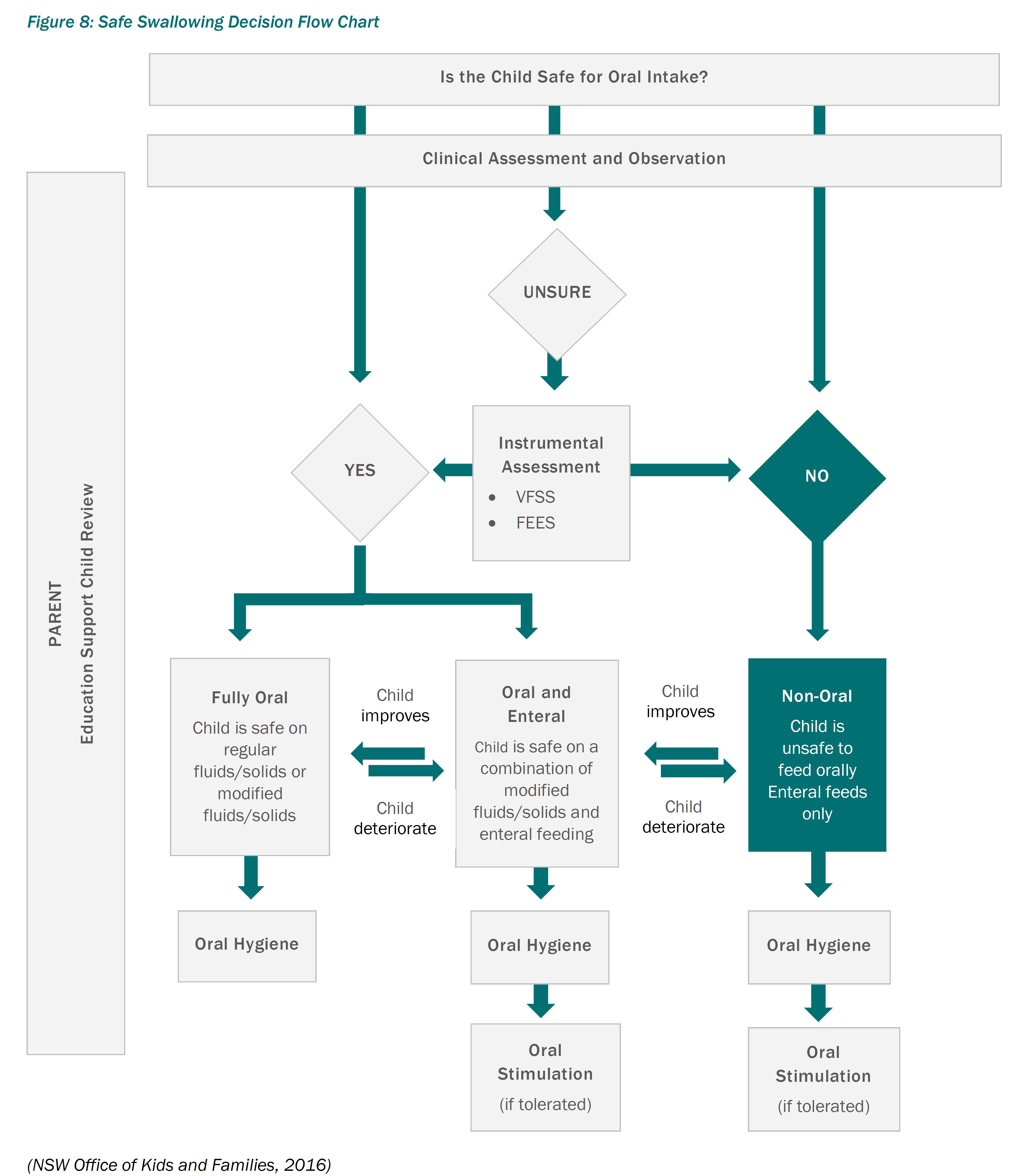
- Facilitating Safe Swallowing
-
Nutrition Management to Improve Oral Nutritional Intake/Nutrition and Hydration
- Estimating Energy and Protein Requirements
- Supporting Adequate Growth
- Supporting Oral Nutrition for Exclusively Breastfed Infants
- Supporting Oral Nutrition for Formula Fed Infants
- Supporting Oral Nutrition for Infants Between 6 - 12 Months
- Supporting Oral Nutrition from 12 Months Onward
- Ensuring Adequate Fluid Intake
- Supporting a Healthy Eating Pattern
- When to Consider Enteral Nutrition
-
Seating and Positioning
- Positioning of Infants and Young Children for Feeding
- Positioning for Breast and Bottle Feeding in Infants and Young Children
- Positioning When Introducing Solids
- Using Highchairs and Boosters
- Positioning for Infants, Children and Youth with Significant Postural Needs
- Using Specialized Seating Equipment
-
Feeding Skill Development
- Facilitating First Tastes
- Facilitating Infant Feeding as a Neurodevelopmental Skill
- Facilitating Child Feeding as a Neurodevelopmental Skill and a Relational and Responsive Process
- Facilitating Oral Sensorimotor Function
- Considerations for Pacifier/Soother Use
- Considerations for Breastfeeding
- Considerations for Bottle Feeding
- Considerations for Solids
- Additional Resources
- Feeding Environments and Routines
- Sensory Processing/Regulation
- Oral Hygiene and Dental Health
- Surgical Management
Facilitating First Tastes
At this stage, the goal of facilitating first tastes is for positive oral feeding experiences, not quantity or nutritional content of intake:
- ensure that the child is awake and able to maintain a quiet alert state before offering tastes
- ensure child can coordinate non-nutritive sucking and breathing before initiating tastes
- children with delayed or disordered oral reflexes, and/or oral sensorimotor dysfunction may require specific treatment techniques, rehabilitation, or teaching new skills, to improve physiology and facilitate oral sensorimotor function
- facilitate midline positioning and flexion that promotes hand to mouth experiences which is an example of feeding readiness
Oral reflexes may be elicited using a number of specific stimuli. The following strategies may be considered when working with parents and infants to facilitate typical oral reflexes:
- aid or arouse the infant into a calm alert state
- in the presence of oral hypersensitivity, systematic desensitization should be considered while addressing oral sensorimotor patterns with oral intake
