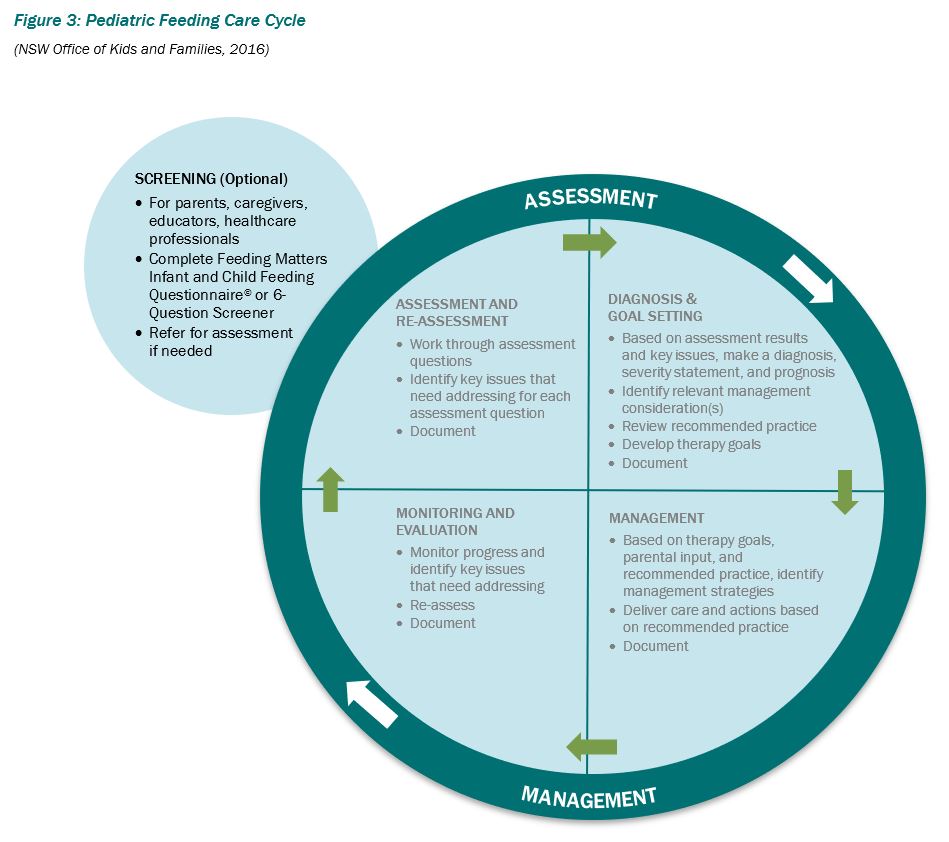
Screening is a strategy used for the purpose of investigation, and is positioned alongside the Pediatric Feeding Care Cycle as an optional precursor to assessment and management (see Figure 3):
This section of the guide includes screening considerations related to:
- the purpose of feeding and swallowing screening
- screening tools
Feeding screening may identify the risk of pediatric feeding disorder (PFD) so that infants, children and youth may be referred for a comprehensive assessment. Screening is not diagnostic and outcomes do not provide information about feeding difficulty severity or best management. Screening is carried out for the purpose of early identification that can support opportunities for a diagnosis and effective treatment, counselling, and education (World Health Organization, 2008). Screening is not the only pathway to an assessment and is not required prior to an assessment. There is no evidence to suggest an optimal time to screen a child for feeding difficulties. Concerned parents will typically identify if their child has difficulty eating, feeding and swallowing, and will bring their child for assessment when concerned about their child meeting their developmental milestones. Parents are advised to talk to a healthcare provider knowledgeable about feeding if they have concerns. CONSIDERATIONS FOR FEEDING SCREENING: Who should be screened? Who could initiate a discussion for need of a feeding screen? Who could complete a feeding screen? Validated tools for screening feeding risk serve to: Multiple screening tools and methods exist to screen feeding risk. The recommended screening tools in this CPG include: The recommended screening tool in this CPG is the Feeding Matters Infant and Child Feeding Questionnaire© (Silverman, Berlin, & Linn, 2020): • the Feeding Matters Infant and Child Feeding Questionnaire© (ICFQ ©) (Silverman, Berlin, & Linn, 2020) Swallowing screening identifies those infants, children and youth with the greatest risk of having swallowing difficulties so that they may be referred for a clinical swallow evaluation or instrumental swallowing evaluation if indicated. By definition, screening is not diagnostic. Unlike clinical or instrumental swallowing evaluations, screening does not provide information about airway protection, dysphagia severity or best management. (American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, 2019); (American Speech, Language, & Hearing Association, 2004); (Swigert, 2019). CONSIDERATIONS FOR SWALLOWING SCREENING Who should be screened? Who could initiate a discussion for need of a swallowing screen? Who could complete a swallowing screen? Validated tools that screen for swallowing risk serve to (Speech Pathology Australia, 2012); (Stewart, 2003): Recommended tools for families to screen for swallowing risk include: Table 1: Indicators that Child is at Risk or may be Aspirating Signs and Indicators of Possible Aspiration OVERT SIGNS SUBTLE SIGNS (NSW Office of Kids and Families, 2016) Note: Aspiration can also occur in the absence of signs or symptoms.What is the Purpose of a Feeding Screening?
Screening Tools for Feeding Risk
• the Feeding Matters Infant and Child Feeding Questionnaire© 6-Question Screener (Silverman, Berlin, & Linn, 2020)What is the Purpose of a Swallowing (Dysphagia) Screening?
Screening Tools for Swallowing (Dysphagia) Risk
(consider secretions, solids eaten and liquids taken orally or by tube):
Any observation of the preceding should be referred immediately for further investigation.
Multiple screening tools and methods exist to screen feeding and swallowing risk. AHS recommends the Feeding Matters Infant and Child Feeding Questionnaire©:
|
Start
|
Start QuestionnaireNote: this link will direct you to Feeding Matters in the United States. After completing the Feeding Matters Infant and Child Feeding Questionnaire©, please return to this website and click on Find Services to locate services in Alberta |
For Families:
The following link can be shared with families and will also direct them to the Feeding Matters Infant and Child Feeding Questionnaire©
